Pain On Top Of The Foot
If you suspect a Lisfranc injury or even a midtarsal joint sprain, then seek medical advice immediately.
Why does the top of my foot hurt?
The foot has a complex set of tendons, muscles, joints, and bones that enable it to work properly, as well as withstand walking, standing, and other everyday movements.
Many health conditions and injuries, however, can upset the foot’s movement and balance, causing problems and pain.
Pain on top of the foot may seem like an unusual location, particularly if no obvious injury took place there. However, this area can be affected by a variety of conditions and injuries beyond a bone fracture or bruise.
Most foot pain requires, at the very least, rest and extra care to heal. If the pain is due to an underlying health condition, additional medical care may be needed.
Taking note of the pain and symptoms and what came before the problem can help determine the cause. This ensures that correct treatment can be given.
An injury, such as a sprain or bone break, can occur in any part of the foot, including the top.
Problems with the top of the foot can be due to dropping something on the area. There can be other, less obvious causes, however.
Lisfrank or midfoot injury

The middle of the foot is known as the Lisfrank area or midfoot. This area is made up of a group of small bones that help form the foot’s arch.
If one of the midfoot bones is broken or a tendon is inflamed or torn, it may cause pain, swelling, bruising, and redness on the top of the foot.
Midfoot injuries can be caused by accidents, such as a heavy object landing on the foot.
Not all midfoot injuries are due to dropping something or getting the foot stepped on, however. They often occur when someone falls with the foot flexed downward, pulling or straining tendons or fracturing bones.
A hairline or stress fracture can also happen in this area due to overuse, such as from long periods of running or high-impact activity.
Midfoot injuries can be mild to severe, depending on how many tendons or bones are injured. Mild tendon injuries may only require RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) until the tendon has healed.
Severe injuries and bone fractures may require a cast, physical therapy, or surgery.
Fracture of fifth metatarsal
Pain on the outside of the top of the foot is often related to the fifth metatarsal. This is a long bone that connects the little toe to the middle of the foot.
Several types of fractures may occur in the fifth metatarsal:
- Avulsion fracture: This occurs when a tendon or ligament pulls a small piece of the fifth metatarsal out of place. An avulsion fracture often occurs with an “ankle roll” injury and may happen along with an ankle sprain.
- Jones fracture: This type of break often occurs near the top of the fifth metatarsal, close to the outside and middle area of the foot. It can be a small hairline fracture caused by repeated stress and strain on the foot, or it can be a more severe break due to an injury or fall.
- Midshaft fracture: This type of break is often due to an accident or twisting of the foot. It occurs near the middle of the fifth metatarsal.
Fifth metatarsal breaks usually require medical care. Staying off the foot and using RICE is recommended right after the injury. Additional care, such as a cast, boot, or crutches, may also be required.
Surgery can be recommended if:
- the bone is displaced
- there are multiple breaks in the fifth metatarsal or other areas of the foot
- the fracture is not healing as expected
Extensor tendinitis

Tendinitis can occur in many different areas of the feet and legs. The extensor tendons, located in the top of the foot, are needed for flexing or pulling the foot upward.
If they become inflamed due to overuse or wearing shoes without proper support, they may get torn or inflamed. This is known as extensor tendinitis, which can cause significant pain in the top of the foot.
Extensor tendinitis pain usually gets worse with activity, and may also occur alongside swelling of the top of the foot. It may come about after excessive exercise or doing too much exercise, too soon.
The condition can be quite painful, but can often be treated with:
- rest, with or without splinting
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen
- steroid injections
- physical therapy or exercises
Once the tendon feels better, it is best to ease back into activity slowly to avoid inflaming or injuring the tendon again.
Ganglion cyst
A ganglion cyst forms below the surface of the skin, appearing like a bump or sac filled with fluid.
It often forms on top of the foot and may happen after an injury to the area. The cause of these cysts, however, is not always known.
A ganglion cyst can cause pain if it is pressing against a muscle or joint in the foot. It may also cause tingling or burning if it is located near a nerve. If the cyst is large, it can cause discomfort or pain when it rubs against shoes.
Treatment for a ganglion cyst depends on how much pain it causes:
- Small cysts that are not causing pain can follow a “wait and see” approach.
- Pads or special footwear can be used to avoid rubbing and irritation of the cyst.
- A cyst can be aspirated, where the fluid is removed with a needle. Sometimes, however, the cyst comes back after this treatment.
- Severe, painful cysts can be removed with surgery.
Pain On Top Of The Foot
Extensor tendonitis is inflammation of the extensor tendons which run along the top of the foot. A more accurate term is tendinopathy which refers to damage or degeneration of the tendon. It is an overuse injury with symptoms including:
- Pain over the top of your foot.
- Symptoms will have occurred gradually over time rather than from a single traumatic incident.
- You might complain of an aching pain on top of the foot, made worse with running and improves with rest.
- There may also be swelling or redness over the top of your foot.
- More on Extensor tendonitis

Arch Support Insoles
Lisfranc Injury
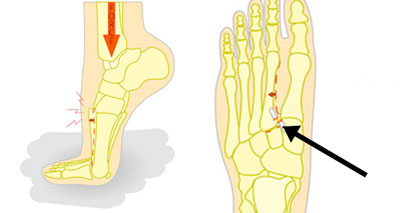
Lisfranc injury is a dislocation or fracture in the midfoot area, and if missed can have serious long-term implications. It occurs in the middle of the foot at the joint where the short tarsal bones meet the long metatarsal bones in the foot. Symptoms include:
- Pain in the midfoot area.
- You will have difficulty putting any weight on the foot.
- In particular, going up onto your toes will be painful.
- There may be some bone deformity visible but not always.
- Swelling is likely on the top of the foot and there will be tenderness over the joint area.
If you suspect a Lisfranc injury or even a midtarsal joint sprain, then seek medical advice immediately.
Midtarsal Joint Sprain
A midtarsal joint sprain is an injury or tear to any of the ligaments holding the midtarsal bones together. The symptoms and severity of a midtarsal joint sprain will depend on which ligaments have been sprained.
- Pain will be felt on the outside middle of the foot.
- There may be swelling on the outside and/or top of the foot.
- Certain movements will trigger pain but the precise location of the pain will depend on which ligaments are injured.
- This injury is rare but can occur in gymnasts, footballers, and jumpers.
With any midfoot sprain or fracture, it is important to consider a Lisfrancs injury which can have serious long-term implications if missed.
Navicular stress fracture
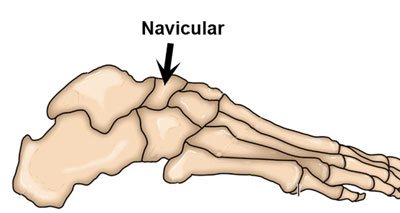
A navicular stress fracture is a hairline fracture of one of the tarsal bones called the Navicular. It is one of the most common stress fractures affecting athletes, especially those in explosive sprinting and jumping-type sports. Symptoms include:
- A poorly localized ache in the midfoot area which gets worse with exercise.
- Pain may radiate along the inside arch of the foot.
- Pressing into the top of the foot over the Navicular bone itself (called the N spot) will be painful and tender.
- More on Navicular stress fracture
Mortons Neuroma
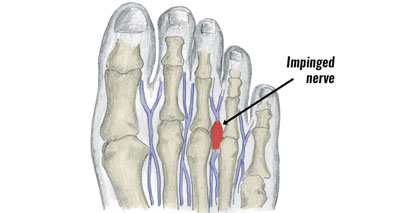
Morton’s neuroma or Morton’s syndrome occurs when a nerve becomes trapped between the third and fourth toes. Symptoms include:
- Pain, numbness, and a tingling sensation over the top of the forefoot.
- Pain is made worse by weight-bearing, particularly up onto the toes.
- Symptoms can also be reproduced by squeezing the forefoot to further compress the nerve.
- More on Mortons neuroma
When should I see a doctor?
If any of the following apply then seek professional medical advice:
If you have severe pain or swelling and are unable to complete normal daily tasks three days after injury.
Or if you have any change in sensation in your foot. For example, numbness, or pins and needles then also seek medical advice.
If you have rested and applied the PRICE principles for two weeks and still have pain or weakness.
External links
Top of Foot Pain
Tim Petrie, DPT, OCS, is a board-certified orthopedic specialist who has practiced as a physical therapist for more than a decade.
Published on August 31, 2022
Adam H. Kaplan, DPM, is a podiatrist who has been in private practice for over 5 years in New Jersey and specializes in a wide scope of foot care.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
With its 26 bones, 30 joints, and over 100 ligaments, muscles, and tendons, the foot is an extremely intricate structure. Because of this complex nature, it can be difficult to determine the exact cause of pain on the top (dorsal) part of the foot.
Paying attention to the details of your condition can help you get to the bottom of the soreness.
This article will detail the most common causes of pain on the top of the foot, the typical symptoms accompanying it, and the various treatments available for it.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/topoffoot-8e162f095cd74a0fbcf94b174bd4f2f6.jpg)
Dorsal Foot Pain Symptoms
Depending on the origins of your dorsal foot pain, several other corresponding symptoms may also be present in this area. These include, but are not limited to:
- Redness or warmth in the forefoot or toes
- Extreme sensitivity and difficulty putting on a sock or shoe
- Swelling in the foot, ankle, or toes
- A palpable nodule on the top of the foot
- Limited range of motion in the foot or toes
- Difficulty standing, walking, or climbing stairs
- Numbness or tingling in the foot or toes
- Bruising on the bottom of the foot
Some of these symptoms are unique to a particular diagnosis, while others can be seen with numerous causes of dorsal foot pain. A formal evaluation by a healthcare provider is the most accurate way to determine a true diagnosis. That said, keeping track of your symptoms and when they originated can help you hone in on the potential cause of your condition.
Causes of Top of Foot Pain
While many conditions can lead to pain on the top of the foot, several are more common. The typical causes of this issue can generally be divided between acute (or repetitive) injuries and more chronic health concerns. Among the more frequently seen acute causes are:
- Metatarsal stress fractures
- Lisfranc injuries
- Extensor tendinitis
When talking about dorsal foot pain from a more chronic medical condition, the most common causes are:
- Gout
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Ganglion cysts
- Midfoot osteoarthritis
- Neuritis (inflammation of a nerve)
Injuries to the top of the foot usually happen during a distinct painful event or due to excessive repetitive activities (like running). For example, Lisfranc injuries occur when the midfoot joints dislocate after the ligaments in this region are torn. This injury commonly happens when the foot is in a downward pointed (plantarflexed) position, and someone lands on top of it. It can also occur after an auto accident or a fall.
Overuse injuries usually occur over time after the volume or intensity of a repetitive activity (like running or jumping) is quickly increased. This can include extensor tendonitis, where the tendons that help lift the foot and toes become overused and painful, or metatarsal stress fractures, where a small crack gradually develops in one of the bones at the base of your toes.
In the case of chronic health conditions that lead to dorsal foot pain, the causes are more varied. For example, gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that leads to sudden, severe pain in the foot or base of the big toe. This condition occurs when high levels of uric acid cause a buildup of irritating urate crystals in a joint.
Midfoot osteoarthritis, on the other hand, is a more localized version of arthritis. This arises when degeneration in the smooth articular cartilage at the ends of the foot bones causes a gradual increase in friction, swelling, and soreness in the region.
Peripheral neuropathy can have numerous causes. Among the most common is diabetes; however, hormone imbalances or kidney dysfunction can also be to blame. This issue can lead to intermittent pain or cramping in the midfoot, along with numbness, tingling, weakness, loss of sensation, or even balance impairments. As it progresses, this condition can ultimately affect numerous parts of the body at the same time.
Finally, the causes of ganglion cysts are not entirely clear. This fluid-filled prominence develops gradually and can occur in many places, including the top of the foot. While typically asymptomatic, occasionally the cyst can cause tingling if it presses on a nerve or soreness if it contacts a tendon or joint.
How to Treat Top of Foot Pain
Some conditions that cause pain on the top of the foot can be treated with common at-home remedies. For example, avoiding irritating activities and using ice and NSAID medication can help improve the symptoms of extensor tendonitis or midfoot arthritis. This same treatment is also commonly needed for metatarsal stress fractures, along with using crutches to avoid weight-bearing through the injured area.
Other conditions require the use of prescription medications. A gout flare-up, for instance, is typically treated with colchicine, a medication that helps lower uric acid levels, or oral steroids. Certain classes of medication, including anti-seizure, antidepressant, and antiarrhythmic drugs, are also commonly used to address peripheral neuropathy.
Finally, a more invasive intervention may also be utilized for your dorsal foot pain in certain situations. For example, the pain from gout or midfoot arthritis is occasionally severe and needs to be treated with a pain-relieving cortisone injection. Surgeries may also be needed in some cases, including many types of Lisfranc injuries, and infrequently for midfoot arthritis or certain types of stress fractures.
Orthotics (shoe inserts) may also be used along with Voltaren gel to help alleviate some of the pain.
Are There Tests to Diagnose the Cause of Top of Foot Pain?
Diagnosis of dorsal foot pain typically begins with a comprehensive evaluation by a physician. During this examination, several tests can help your healthcare provider discover the root cause of your issue:
- X-rays and MRIs: These tests are useful for visualizing bone and soft tissue conditions like midfoot arthritis, a stress fracture, a Lisfranc injury, or extensor tendonitis. This type of imaging may also be used for a ganglion cyst, though this is rarer.
- Blood Draws: Assessing your body’s uric acid levels using a blood draw may be necessary if gout is suspected.
- EMG: This test assesses how well the nerves in your leg and foot are functioning and can help diagnose peripheral neuropathy.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
Any new or worsening pain on the top of the foot should be examined by your healthcare provider as soon as possible. While at-home remedies may help alleviate your symptoms, this improvement may be temporary. In addition, some diagnoses like a stress fracture, gout, or peripheral neuropathy may progress or worsen if treated inappropriately.
Because of this, it is important to seek the care of a healthcare provider if you are experiencing any of the symptoms detailed above. This is especially important if you have other health conditions like diabetes, osteoporosis, kidney dysfunction, or vitamin or hormone deficiencies which can exacerbate some of the conditions that cause pain on the top of the foot.
Summary
Top of the foot pain can be caused by many things, including chronic health conditions and more acute injuries. Along with soreness, other symptoms like swelling, stiffness, numbness, tingling, or bruising may also be present in the region.
A wide variety of treatments like anti-inflammatory medication, activity modification, injections, or even surgery may be needed depending on the underlying source of your condition. Due to the numerous potential causes, a healthcare provider should evaluate any new or worsening dorsal foot pain.
A Word From Verywell
Dealing with pain on the top of the foot, especially if it appears suddenly or is intense, can be an unnerving experience. However, while your mind may immediately go to the worst-case scenario, dorsal foot symptoms can be easily and effectively treated in many situations.
Tell your healthcare provider about your situation if you experience an acute injury or a new onset of pain in this area. Following a comprehensive examination, they’ll be able to guide your recovery from this sometimes disabling issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does a midfoot injury require surgery?
In many cases, injuries that affect the midfoot can be managed conservatively with activity modification, physical therapy, or pain medication. This is true for issues like metatarsal stress fractures, a low-grade Lisfranc injury, extensor tendonitis, or a flare-up of midfoot arthritis. However, some more severe Lisfranc injuries or stress fractures, as well as midfoot arthritis that does not respond to initial treatments, may require surgery.
Is peripheral neuropathy curable?
Most cases of peripheral neuropathy cannot be cured. Fortunately, there are many things that can be done to help manage the symptoms of this condition. This may include prescription medication, lidocaine patches, or a pain-relieving injection or nerve surgery.
Could the pain in the middle of my foot be gout?
While gout most commonly affects the outer base of the first toe, it can also target the foot or ankle regions (along with many other joints in the body). The pain from gout is typically sudden and severe in nature, often appearing for the first time at night. The affected area is also frequently stiff, warm, and swollen. Gout symptoms should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately to initiate treatment.
Verywell Health uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
- Khanna PP, Gladue HS, Singh MK, et al. Treatment of acute gout: a systematic review. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2014;44(1):31-38. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.02.003
- American Association of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Lisfranc (midfoot) injury.
- American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons. Ganglion cyst.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. Peripheral neuropathy.
- American Association of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Stress fractures of the foot and ankle.
- American Medical Society for Sports Medicine. Extensor tendinopathy.
- Massachusetts General Hospital. Midfoot arthritis.
By Tim Petrie, DPT, OCS
Tim Petrie, DPT, OCS, is a board-certified orthopedic specialist who has practiced as a physical therapist for more than a decade.






