Krill Oil Benefits: Superior to Fish Oil
Acute inflammation is a normal immune response that can help protect your body against foreign invaders. Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, is thought to contribute to a range of health conditions, including obesity, diabetes, heart disease and even cancer.
KRILL OIL – Uses, Side Effects, and More
Krill oil comes from a tiny, shrimp-like marine animal. It’s rich in the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
The benefits of krill oil seem to come from its omega-3 fatty acid content. The body doesn’t produce many of its own omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids can reduce pain and swelling and also prevent the blood from clotting easily.
People use krill oil for dry eye. It is also used for high levels of triglycerides in the blood, high cholesterol, diabetes, depression, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support many of these uses.
Don’t confused krill oil with algal oil, cod liver oil, fish oil, or shark liver oil. These are not the same.
How does it work ?
Uses & Effectiveness ?
Possibly Effective for
- Dry eye. Taking krill oil by mouth for about 3 months improves dry eye symptoms such as redness.
Side Effects
When taken by mouth: Krill oil is possibly safe when used for up to 6 months. Side effects might include stomach upset, decreased appetite, heartburn, fishy burps, bloating, diarrhea, and nausea.
Special Precautions and Warnings
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: There isn’t enough reliable information to know if krill oil is safe to use when pregnant or breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
Bleeding disorders: Krill oil can slow blood clotting. It might increase the risk of bleeding in people with bleeding disorders.
Seafood allergy: Some people who are allergic to seafood might also be allergic to krill oil supplements. Avoid using krill oil or use it cautiously if you have a seafood allergy.
Surgery: Krill oil can slow blood clotting. It might increase the risk of bleeding during and after surgery. Stop using krill oil at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Interactions ?
Moderate Interaction
Be cautious with this combination
Medications that slow blood clotting (Anticoagulant / Antiplatelet drugs) interacts with KRILL OIL
Medications for diabetes (Antidiabetes drugs) interacts with KRILL OIL
Dosing
Krill oil has most often been used by adults in doses of 1-4 grams by mouth daily for up to 6 months. Speak with a healthcare provider to find out what dose might be best for a specific condition.
REFERENCES:
Banni, S., Carta, G., Murru, E., Cordeddu, L., Giordano, E., Sirigu, A. R., Berge, K., Vik, H., Maki, K. C., Di, Marzo, V, and Griinari, M. Krill oil significantly decreases 2-arachidonoylglycerol plasma levels in obese subjects. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2011;8(1):7. View abstract.
Gigliotti, J. C., Smith, A. L., Jaczynski, J., and Tou, J. C. Consumption of krill protein concentrate prevents early renal injury and nephrocalcinosis in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Urol.Res 2011;39(1):59-67. View abstract.
Hellgren, K. Assessment of Krillase chewing gum for the reduction of gingivitis and dental plaque. J Clin Dent 2009;20(3):99-102. View abstract.
Ierna, M., Kerr, A., Scales, H., Berge, K., and Griinari, M. Supplementation of diet with krill oil protects against experimental rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet.Disord. 2010;11:136. View abstract.
Kidd, P. M. Krill oil complex: potent nutraceutical synergy. Total Health 2003;25(4):15.
Kidd, P. M. Omega-3 DHA and EPA for cognition, behavior, and mood: clinical findings and structural-functional synergies with cell membrane phospholipids. Altern Med Rev 2007;12(3):207-227. View abstract.
Le, Grandois J., Marchioni, E., Zhao, M., Giuffrida, F., Ennahar, S., and Bindler, F. Investigation of natural phosphatidylcholine sources: separation and identification by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS2) of molecular species. J Agric.Food Chem 7-22-2009;57(14):6014-6020. View abstract.
Maki, K. C., Reeves, M. S., Farmer, M., Griinari, M., Berge, K., Vik, H., Hubacher, R., and Rains, T. M. Krill oil supplementation increases plasma concentrations of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in overweight and obese men and women. Nutr.Res. 2009;29(9):609-615. View abstract.
Winther, B., Hoem, N., Berge, K., and Reubsaet, L. Elucidation of phosphatidylcholine composition in krill oil extracted from Euphausia superba. Lipids 2011;46(1):25-36. View abstract.
Yamada, H., Ueda, T., and Yano, A. Water-soluble extract of Pacific Krill prevents triglyceride accumulation in adipocytes by suppressing PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha expression. PLoS.One. 2011;6(7):e21952. View abstract.
Zhu, J. J., Shi, J. H., Qian, W. B., Cai, Z. Z., and Li, D. Effects of krill oil on serum lipids of hyperlipidemic rats and human SW480 cells. Lipids Health Dis 2008;7:30. View abstract.
Albert BB, Derraik JG, Brennan CM, et al. Supplementation with a blend of krill and salmon oil is associated with increased metabolic risk in overweight men. Am J Clin Nutr 2015;102(1):49-57. View abstract.
Barenie MJ, Freemas JA, Baranauskas MN, et al. Effectiveness of a combined New Zealand green-lipped mussel and Antarctic krill oil supplement on markers of exercise-induced muscle damage and inflammation in untrained men. J Diet Suppl. 2020 Dec 9:1-26. View abstract.
Berge K, Musa-Veloso K, Harwood M, Hoem N, Burri L. Krill oil supplementation lowers serum triglycerides without increasing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in adults with borderline high or high triglyceride levels. Nutr Res 2014;34(2):126-33. View abstract.
Bottino NR. Lipid composition of two species of Antarctic krill: Euphausia superba and E. crystallorophias. Comp Biochem Physiol B 1975;50:479-84. View abstract.
Bunea R, El Farrah K, Deutsch L. Evaluation of the effects of Neptune Krill Oil on the clinical course of hyperlipidemia. Altern Med Rev 2004;9:420-8. View abstract.
Calder PC. N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation and immunity: pouring oil on troubled waters or another fishy tale? Nutr Res 2001;21:309-41.
Connor WE. n-3 Fatty acids from fish and fish oil: panacea or nostrum? Am J Clin Nutr 2001;74;415-6. View abstract.
Deinema LA, Vingrys AJ, Wong CY, Jackson DC, Chinnery HR, Downie LE. A randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled clinical trial of two forms of omega-3 supplements for treating dry eye disease. Ophthalmology. 2017;124(1):43-52. View abstract.
Deutsch L. Evaluation of the effect of Neptune Krill Oil on chronic inflammation and arthritic symptoms. J Am Coll Nutr 2007;26:39-48. View abstract.
Dunlap WC, Fujisawa A, Yamamoto Y, et al. Notothenioid fish, krill and phytoplankton from Antarctica contain a vitamin E constituent (alpha-tocomonoenol) functionally associated with cold-water adaptation. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 2002;133:299-305. View abstract.
Foran SE, Flood JG, Lewandrowski KB. Measurement of mercury levels in concentrated over-the-counter fish oil preparations: is fish oil healthier than fish? Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:1603-5. View abstract.
Goldberg LD, Crysler C. A single center, pilot, double-blinded, randomized, comparative, prospective clinical study to evaluate improvements in the structure and function of facial skin with tazarotene 0.1% cream alone and in combination with GliSODin Skin Nutrients Advanced Anti-Aging Formula. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2014;7:139-44. View abstract.
Harris WS, Miller M, Tighe AP, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids and coronary heart disease risk: clinical and mechanistic perspectives. Atherosclerosis 2008;197:12-24. View abstract.
Kim MG, Yang I, Lee HS, Lee JY, Kim K. Lipid-modifying effects of krill oil vs fish oil: a network meta-analysis. Nutr Rev 2020;78(9):699-708. doi: View abstract.
Köhler A, Sarkkinen E, Tapola N, Niskanen T, Bruheim I. Bioavailability of fatty acids from krill oil, krill meal and fish oil in healthy subjects–a randomized, single-dose, cross-over trial. Lipids Health Dis 2015;14:19. View abstract.
Konagai C, Yanagimoto K, Hayamizu K, et al. Effects of krill oil containing n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in phospholipid form on human brain function: a randomized controlled trial in healthy elderly volunteers. Clin Interv Aging 2013;8:1247-57. View abstract.
Leaf A. On the reanalysis of the GISSI-Prevenzione. Circulation 2002;105:1874-5. View abstract.
Lobraico JM, DiLello LC, Butler AD, Cordisco ME, Petrini JR, Ahmadi R. Effects of krill oil on endothelial function and other cardiovascular risk factors in participants with type 2 diabetes, a randomized controlled trial. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2015;3(1):e000107. View abstract.
Melanson SF, Lewandrowski EL, Flood JG, Lewandrowski KB. Measurement of organochlorines in commercial over-the-counter fish oil preparations: implications for dietary and therapeutic recommendations for omega-3 fatty acids and a review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:74-7. View abstract.
Mozaffarian D, Maki KC, Bays HE, et al. Effectiveness of a Novel ω-3 Krill Oil Agent in Patients With Severe Hypertriglyceridemia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open 2022;5(1):e2141898. View abstract.
Multi-center, double-blind, placebo-controlled, monotherapy study of Neptune Krill oil (NKO) in early stage Alzheimer’s disease. 2009.
Sampalis F, Bunea R, Pelland MF, et al. Evaluation of the effects of Neptune Krill Oil on the management of premenstrual syndrome and dysmenorrhea. Altern Med Rev 2003;8:171-9. View abstract.
Tandy S, Chung RW, Wat E, et al. Dietary krill oil supplementation reduces hepatic steatosis, glycemia, and hypercholesterolemia in high-fat-fed mice. J Agric Food Chem 10-14-2009;57:9339-45. View abstract.
Ulven SM, Kirkhus B, Lamglait A, et al. Metabolic effects of krill oil are essentially similar to those of fish oil but at lower dose of EPA and DHA, in healthy volunteers. Lipids 2011;46:37-46. View abstract.
Ursoniu S, Sahebkar A, Serban MC, Lipid and Blood Pressure Meta-analysis Collaboration Group. Lipid-modifying effects of krill oil in humans: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Rev. 2017;75(5):361-373. View abstract.
van der Wurff ISM, von Schacky C, Bergeland T, et al. Effect of one year krill oil supplementation on depressive symptoms and self-esteem of Dutch adolescents: A randomized controlled trial. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2020;163:102208. View abstract.
Venkatraman JT, Chandrasekar B, Kim JD, Fernandes G. Effects of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids on the activities and expression of hepatic antioxidant enzymes in autoimmune-prone NZBxNZW F1 mice. Lipids 1994;29:561-8. View abstract.
Wakeman MP. An open-label pilot study to assess the effectiveness of krill oil with added vitamins and phytonutrients in the relief of symptoms of PMS. Nutrition Dietary Suppl 2013:5;17-25.
Krill Oil Benefits: Superior to Fish Oil?

Looking to shed a few pounds, improve your skin or keep your brain sharp? You may want to consider taking krill oil. High in both omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, the potential krill oil benefits are pretty impressive.
Krill oil has gained widespread popularity in recent years as a safe and healthy alternative to fish oil. The benefits of krill oil vs. fish oil are nearly identical, but krill oil is more bioavailable, more sustainable, and less likely to be contaminated by mercury or heavy metals.
So what is krill oil made from, how can it affect your health and should you be adding it to your daily routine? Let’s take a look.
What Is Krill Oil?
Krill oil is a supplement extracted from a species of Antarctic krill, which is a small, shrimp-like crustacean found in the Southern Ocean. Situated at the very bottom of the food chain, krill feed primarily on phytoplankton, or microscopic marine algae.
Krill oil contains a highly concentrated amount of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been linked to an extensive list of health benefits, from reduced inflammation to a decreased risk of chronic disease. In addition to omega-3 fatty acids, krill oil also contains phospholipid-derived fatty acids as well as astaxanthin, a potent carotenoid revered for its antioxidant properties.
Krill oil benefits include everything from strengthening bones and joints to boosting brain health and more.
Benefits
1. Fights Inflammation
Acute inflammation is a normal immune response that can help protect your body against foreign invaders. Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, is thought to contribute to a range of health conditions, including obesity, diabetes, heart disease and even cancer.
Krill oil is high in omega-3 fatty acids like docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. According to one study out of the University of Tehran in Iran, supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids for just eight weeks was able to significantly reduce levels of inflammatory markers in the blood. Krill oil also contains astaxanthin, a natural pigment that can help fight the free radicals that cause chronic inflammation.
In addition to lowering the risk of chronic disease, the anti-inflammatory properties of krill oil could have far-reaching benefits that extend to nearly every aspect of health, from slowing aging to protecting against certain autoimmune conditions.
2. Improves Heart Health
Whether you’re looking to drop your cholesterol levels or simply keep your heart in tip-top shape, krill oil may be able to help. Krill oil is jam-packed with omega-3 fatty acids, which have been linked to reduced inflammation, a decreased risk of heart disease and improvements in cardiovascular function.
One 2015 study focused on measuring the krill oil benefits on heart health in people with diabetes. Researchers found that taking 1,000 milligrams of krill oil reduced several heart disease risk factors and even increased levels of beneficial HDL cholesterol.
Meanwhile, other studies have shown that the omega-3 fatty acids found in krill oil can lower heart rate and blood pressure, decrease high triglycerides and reduce the risk of coronary heart disease. Clearly, the omega-3 content plays a huge role in krill oil benefits for the heart.
3. Keeps Skin Glowing
From acne to dermatitis, inflammation is at the root of many common skin conditions. One of the top benefits of krill oil for skin health is its content of omega-3 fatty acids, which have the ability to ease inflammation and keep your skin glowing.
In one study out of South Korea, supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids was found to reduce inflammatory acne by an impressive 42 percent. Another animal study published in the Journal of Medical Investigation also showed that DHA and EPA, two types of omega-3 fatty acids found in krill oil, were able to block the production of a specific molecule involved in inflammation, aiding in the treatment of conditions like atopic dermatitis. (9)
Krill oil also contains astaxanthin, which may help improve skin health even more. According to one study in 2009, oral supplementation paired with topical application of astaxanthin reduced age spots and wrinkles while improving skin texture and moisture content.

4. Benefits Brain Health
The brain-boosting benefits of omega-3 fatty acids have been well-documented. Omega-3 fatty acids are believed to help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety and even slow cognitive decline. Some evidence has also found that omega-3 fatty acids may be beneficial in the treatment of disorders like ADHD, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.
There is less research on the cognitive effects of krill oil specifically, but several studies have turned up promising results. A 2013 animal study, for example, showed that krill oil enhanced cognition and exhibited antidepressant effects in rats. Plus, another study showed that 12 weeks of supplementation with krill oil helped activate cognitive function in elderly men.
5. Supports Strong Bones and Joints
Aging can take a big toll on your body, especially in the bones and joints. Conditions like osteoporosis and arthritis become increasingly prevalent with age as you begin to lose bone density and cartilage, causing symptoms like pain, stiffness and an increased risk of fractures.
Some evidence suggests that the omega-3 fatty acids found in krill oil could help keep your bones and joints healthy and strong. Studies show that omega-3 fatty acids can help preserve bone density and reduce the inflammation that contributes to bone and joint pain. More research is needed to evaluate the effects of krill oil in particular on bone and joint health, but the omega-3 in krill oil benefits bone health.
6. May Be Associated with Reduced Cancer Risk
As if you needed another reason to get in your daily dose of krill oil, some research shows that omega-3 fatty acids could be associated with a decreased risk of certain types of cancer.
In particular, studies have found that a higher intake of omega-3 fatty acids from supplementation or fish consumption may be associated with a reduced risk of prostate and breast cancer. A study published in the European Journal of Cancer Prevention also found that higher consumption of omega-3 fatty acids was associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer.
However, keep in mind that these studies show an association but don’t take into account other factors that may play a role. More research is needed to determine how krill oil and omega-3 fatty acid intake may directly affect cancer development.
7. Aids in Weight Loss
Research shows that krill oil benefits weight loss, thanks to its omega-3 fatty acid content. In fact, studies have found that omega-3 fatty acids could help reduce appetite, kick up metabolism and rev up fat burning.
One study published in Appetite showed that consuming at least 1.3 grams of omega-3 fatty acids daily increased feelings of satiety up to two hours after a meal. Other studies have found that omega-3 fatty acids can increase metabolism between 4 percent to 14 percent and amp up the amount of fat burned during exercise by up to 27 percent.
Interactions, Precautions and Side Effects
Despite the many krill oil benefits, it may not be for everyone. If you’re allergic to crustaceans or seafood, you definitely want to skip krill oil. If you have a shellfish allergy, you should also hold off on taking krill oil until you talk to your doctor. Watch out for food allergy symptoms like abdominal pain, swelling, itching or hives, and report any adverse side effects to a trusted health care practitioner.
The omega-3 fatty acids found in krill oil can slow blood clotting. If you take blood thinners like warfarin, discuss with your doctor before taking krill oil as it may interfere with the effectiveness of your medications. Additionally, you may need to discontinue taking krill oil at least two weeks before undergoing surgery to prevent adverse side effects.
When first starting out, krill oil can cause side effects like nausea, belching, bad breath and dyspepsia. Other krill oil side effects heartburn, indigestion, stomach discomfort and a fishy aftertaste. These issues are especially common when you first start taking krill oil and decrease gradually over time.
To minimize symptoms, opt for a high-quality, pharmaceutical grade krill oil, take it with a meal, start with a low dose and increase your intake slowly.
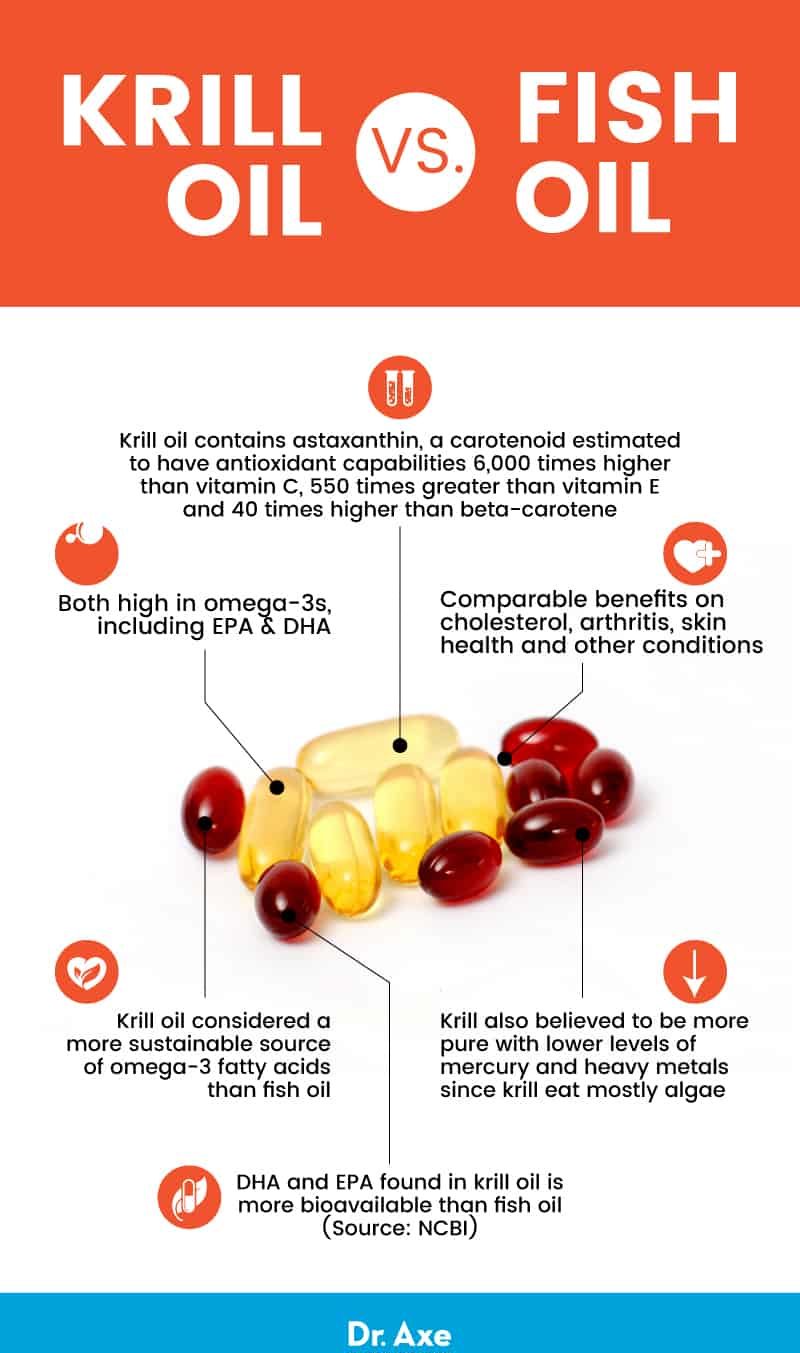
Krill Oil vs. Fish Oil
Both krill oil and fish oil are high in beneficial omega-3 fatty acids, including EPA and DHA. Therefore, the benefits of krill oil vs. fish oil for cholesterol, arthritis, skin health and other conditions are pretty comparable.
The main benefit of krill oil over fish oil is its absorbability. In fact, a multitude of studies have compared the bioavailability of fish oil versus krill oil over the years. One large review out of Norway, for instance, compiled the results of 14 studies and showed that the DHA and EPA found in krill oil was more bioavailable than fish oil.
Additionally, krill oil contains the added bonus of astaxanthin, a carotenoid found in a variety of foods with powerful antioxidant properties. Also known as “the king of carotenoids,” astaxanthin’s ability to fight free radicals is estimated to be 6,000 times higher than vitamin C, 550 times greater than vitamin E and 40 times higher than beta-carotene.
Krill oil is also believed to be more pure, with lower levels of mercury and heavy metals than fish oil. Because krill consume algae, they are much less likely to accumulate high amounts of these contaminants than other types of fish.
Finally, krill oil is considered a more sustainable source of omega-3 fatty acids than fish oil. This is because Antarctic krill are one of the most abundant animal species on Earth. Opting for krill oil instead of fish oil can help ensure that you’re not contributing to unsustainable and harmful practices like overfishing.
How to Use
Krill oil is widely available at most pharmacies, health food stores and online retailers, usually right next to the fish oil and other omega-3 fatty acid supplements.
Be sure to buy from a trusted, reputable brand, and look for supplements that contain a high amount of EPA and DHA with minimal fillers or added ingredients to make sure you get the best krill oil supplement.
When starting out, begin with a lower dose of krill oil and increase your intake slowly over the next few days to assess your tolerance and minimize any potential negative side effects.
Taking krill oil with a meal can also help reduce some of the negative symptoms like belching or fishy aftertaste. You can take it at any time of the day, but many people prefer taking it first thing in the morning alongside a healthy breakfast.
Dosage
Wondering how much take if you’re looking to maximize krill oil benefits? Most studies use a krill oil dosage between 1,000–3,000 milligrams daily, although this amount can vary widely based on the amount of EPA and DHA present in your supplement.
In general, however, the majority of health organizations seem to agree that lower doses of 250–500 milligrams of combined EPA and DHA can be beneficial for most health conditions. Be sure to look closely at the label of your supplement to check how much EPA and DHA it contains; even if a supplement contains 1,000 milligrams of krill oil, the amount of EPA and DHA may be much lower.
Additionally, be sure to start with a lower dose and work your way up. Not only does this ensure that you’re able to tolerate krill oil, but it can also reduce the risk of unpleasant symptoms like belching and nausea.
History
Commercial krill fishing dates back to the 1970s, and krill oil was originally approved as a nutraceutical supplement by the FDA nearly 20 years ago, in 1999. Still, krill oil has only gained traction in recent years as a sustainable alternative to fish oil.
Antarctic krill are one of the most abundant animal species on Earth, with scientists estimating that there are nearly 500 million tons found in the Southern Ocean. Female krill can lay up to 10,000 eggs at a time and can lay eggs several times each season.
Krill are also incredibly resilient. During the winter when food is scarce, they manage to find other food sources, like the algae that grows underneath the surface of the ice, on the ocean floor or even on other animals. In tough times, krill can survive up to 200 days without food.
However, krill are also an essential part of our ecological community. Because many other species depend on krill to survive, organizations like the Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources help sustain the delicate balance of the ocean’s ecosystem by setting krill catch limits to prevent overfishing.
Final Thoughts
- Krill oil is extracted from a species of Antarctic krill, a shrimp-like crustacean found in abundance throughout the Southern Ocean.
- In addition to being loaded with omega-3 fatty acids, krill oil is also high in astaxanthin and phospholipid-derived fatty acids, which help provide a host of krill oil benefits.
- Krill oil benefits include reduced inflammation; improvements in heart, skin and brain health; stronger bones and joints; and increased weight loss. It may also be associated with a lower risk of certain types of cancer.
- Compared to fish oil, krill oil is more absorbable, less likely to be contaminated by heavy metals and considered to be more sustainable.
- For best results, aim to get in between 250–500 milligrams of combined EPA and DHA daily, whether it’s from krill oil, fish oil or whole food sources.
Popular Nutrition Posts






