Acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking other products that cause drowsiness such as opioid pain or cough relievers (such as codeine, hydrocodone), alcohol, marijuana (cannabis), other drugs for sleep or anxiety (such as alprazolam, lorazepam, zolpidem), muscle relaxants (such as carisoprodol, cyclobenzaprine), or antihistamines (such as cetirizine, diphenhydramine).
Butalbital/Acetamin/Caffeine Tablet – Uses, Side Effects, and More
One ingredient in this product is acetaminophen. Taking too much acetaminophen may cause serious (possibly fatal) liver disease. Adults should not take more than 4000 milligrams (4 grams) of acetaminophen a day. People with liver problems and children should take less acetaminophen. Ask your doctor or pharmacist how much acetaminophen is safe to take.
Do not use with any other drug containing acetaminophen without asking your doctor or pharmacist first. Acetaminophen is in many nonprescription and prescription medications (such as pain/fever drugs or cough-and-cold products). Check the labels on all your medicines to see if they contain acetaminophen, and ask your pharmacist if you are unsure.
Get medical help right away if you take too much acetaminophen (overdose), even if you feel well. Overdose symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, sweating, stomach/abdominal pain, extreme tiredness, yellowing eyes/skin, and dark urine.
Daily alcohol use, especially when combined with acetaminophen, may damage your liver. Avoid alcohol.
Warnings:
One ingredient in this product is acetaminophen. Taking too much acetaminophen may cause serious (possibly fatal) liver disease. Adults should not take more than 4000 milligrams (4 grams) of acetaminophen a day. People with liver problems and children should take less acetaminophen. Ask your doctor or pharmacist how much acetaminophen is safe to take.
Do not use with any other drug containing acetaminophen without asking your doctor or pharmacist first. Acetaminophen is in many nonprescription and prescription medications (such as pain/fever drugs or cough-and-cold products). Check the labels on all your medicines to see if they contain acetaminophen, and ask your pharmacist if you are unsure.
Get medical help right away if you take too much acetaminophen (overdose), even if you feel well. Overdose symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, sweating, stomach/abdominal pain, extreme tiredness, yellowing eyes/skin, and dark urine.
Daily alcohol use, especially when combined with acetaminophen, may damage your liver. Avoid alcohol.
Uses
This combination medication is used to treat tension headaches. Acetaminophen helps to decrease the pain from the headache. Caffeine helps increase the effects of acetaminophen. Butalbital is a sedative that helps to decrease anxiety and cause sleepiness and relaxation.
How to use Butalbital/Acetamin/Caffeine Tablet
See also Warning section.
Take this medication by mouth with or without food as directed by your doctor, usually every 4 hours as needed.
If you are using the liquid form of this medication, carefully measure the dose using a special measuring device/spoon. Do not use a household spoon because you may not get the correct dose.
The dosage is based on your medical condition, age, and response to treatment. This medication works best if it is used as the first signs of a headache occur. If you wait until the headache has worsened, the medication may not work as well.
If you suddenly stop using this medication, you may have withdrawal symptoms (such as nausea/vomiting, mental/mood changes, seizures). To help prevent withdrawal, your doctor may lower your dose slowly. Withdrawal is more likely if you have used this medication for a long time or in high doses. Tell your doctor or pharmacist right away if you have withdrawal.
Though it helps many people, this medication may sometimes cause addiction. This risk may be higher if you have a substance use disorder (such as overuse of or addiction to drugs/alcohol). Take this medication exactly as prescribed to lower the risk of addiction. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more details.
Tell your doctor if you notice increased use of this medication, a worsening of headaches, an increase in the number of headaches, the medication not working as well, or use of this medication for more than 2 headache episodes a week. Do not take more than recommended. Your doctor may need to change your medication and/or add a separate medication to prevent the headaches.
Side Effects
See also Warning section.
Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation, dry mouth, shaking (tremor), shortness of breath, increased urination, lightheadedness, dizziness, drowsiness, or trouble sleeping may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
To reduce your risk of dizziness and lightheadedness, get up slowly when rising from a sitting or lying position.
Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.
Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: mental/mood changes, fainting, seizures, fast/irregular heartbeat.
A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
In the US – Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.
In Canada – Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
Precautions
See also Warning section.
Before taking this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to acetaminophen, caffeine, or butalbital; or to other barbiturates (such as phenobarbital) or xanthine derivatives (such as theophylline); or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.
Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: severe breathing problems (such as bronchopneumonia), a certain enzyme disorder (porphyria), liver disease, kidney disease, personal or family history of a substance use disorder (such as overuse of or addiction to drugs/alcohol), mental/mood disorders, abdominal/stomach problems (such as stomach ulcer).
This drug may make you dizzy or drowsy. Alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) can make you more dizzy or drowsy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do anything that needs alertness until you can do it safely. Avoid alcoholic beverages. Talk to your doctor if you are using marijuana (cannabis).
Liquid products may contain alcohol, sugar and/or aspartame. Caution is advised if you have diabetes, alcohol dependence, liver disease, phenylketonuria (PKU), or any other condition that requires you to limit/avoid these substances in your diet. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about using this product safely.
Before having surgery or certain medical procedures (such as a heart stress test or a procedure to restore a normal heart rhythm if you have an unusually fast heartbeat), tell your doctor or dentist that you use this medication and about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).
Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially drowsiness and trouble falling asleep. These side effects can increase the risk of falling.
During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. Using it for long periods or in high doses near the expected delivery date is not recommended because of possible harm to the unborn baby. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor. Infants born to mothers who have used this medication for an extended time may have withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, abnormal/nonstop crying, vomiting, seizures, or diarrhea. Tell your doctor right away if you notice any of these symptoms in your newborn.
This drug passes into breast milk and could have undesirable effects on a nursing infant. Consult your doctor before breast-feeding.
Interactions
See also Warning section.
Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor’s approval.
Some products that may interact with this drug include: darunavir, sodium oxybate, isoniazid, ketoconazole, levoketoconazole, lithium, phenothiazines (such as chlorpromazine).
This drug can speed up the removal of other drugs from your body by affecting certain liver enzymes. These affected drugs include doxycycline, estrogen, felodipine, lonafarnib, quinidine, rilpivirine, tamoxifen, theophylline, voriconazole, “blood thinners” (such as warfarin), certain beta blockers (such as metoprolol), corticosteroids (such as prednisone), among others.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking other products that cause drowsiness such as opioid pain or cough relievers (such as codeine, hydrocodone), alcohol, marijuana (cannabis), other drugs for sleep or anxiety (such as alprazolam, lorazepam, zolpidem), muscle relaxants (such as carisoprodol, cyclobenzaprine), or antihistamines (such as cetirizine, diphenhydramine).
Check the labels on all your medicines (such as allergy or cough-and-cold products) because they may contain caffeine or ingredients that cause drowsiness. Also keep in mind that certain beverages (such as coffee, colas, tea, energy drinks) contain caffeine. Ask your pharmacist about using those products safely.
This medication may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal birth control such as pills, patch, or ring. This could cause pregnancy. Discuss with your doctor or pharmacist if you should use additional reliable birth control methods while using this medication. Also tell your doctor if you have any new spotting or breakthrough bleeding, because these may be signs that your birth control is not working well.
This medication may interfere with certain medical/laboratory tests, possibly causing false test results. Make sure laboratory personnel and all your doctors know you use this drug.
Acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine
Generic name: acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine [ a-SEET-a-MIN-oh-fen, bue-TAL-bi-tal, and-KAF-een ]
Brand names: Esgic, Fioricet, Zebutal, Esgic-Plus, Arcet, . show all 37 brands Isocet, Pharmagesic, Anoquan, Two-Dyne, Tenake, Margesic, Anolor 300, Femcet, Geone, Tencet, Triad, Fiorpap, Repan, Dolmar, Endolor, Ezol, Ide-cet, G-1, Medigesic, Minotal, Mygracet, Pacaps, Alagesic, Americet, Nonbac, Dolgic LQ, Dolgic Plus, Orbivan, Capacet, Vanatol LQ, Vanatol S, Vtol LQ
Dosage forms: oral capsule (300 mg-50 mg-40 mg; 325 mg-50 mg-40 mg); oral liquid (325 mg-50 mg-40 mg/15 mL); oral tablet (325 mg-50 mg-40 mg)
Drug class: Analgesic combinations
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com on Jan 21, 2022. Written by Cerner Multum.
What is acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine?
Acetaminophen is a pain reliever and fever reducer.
Butalbital is in a group of drugs called barbiturates. It relaxes muscle contractions involved in a tension headache.
Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant. It relaxes muscle contractions in blood vessels to improve blood flow.
Acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine is a combination medicine used to treat tension headaches that are caused by muscle contractions.
Acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
Warnings
Do not use this medcine if you have used an MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days. A dangerous drug interaction could occur. MAO inhibitors include isocarboxazid, linezolid, methylene blue injection, phenelzine, and tranylcypromine.
Do not take more of this medication than is recommended. An overdose of acetaminophen can damage your liver or cause death. Call your doctor at once if you have nausea, pain in your upper stomach, itching, loss of appetite, dark urine, clay-colored stools, or jaundice (yellowing of your skin or eyes).
In rare cases, acetaminophen may cause a severe skin reaction. Stop taking acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine and call your doctor right away if you have skin redness or a rash that spreads and causes blistering and peeling.
Before taking this medicine
Do not use this medicine if you have taken an MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days. A dangerous drug interaction could occur. MAO inhibitors include isocarboxazid, linezolid, phenelzine, rasagiline, selegiline, and tranylcypromine.
You should not use acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine if you are allergic to it, if you have porphyria, or if you have recently used alcohol, sedatives, tranquilizers, or other opioids.
Tell your doctor if you have ever had:
- liver disease, cirrhosis, a history of alcoholism or drug addiction, or if you drink more than 3 alcoholic beverages per day;
- kidney disease;
- stomach ulcer or bleeding;
- a history of skin rash caused by any medication; or
- a history of mental illness or suicidal thoughts.
It is not known whether this medicine will harm an unborn baby. If you use butalbital while you are pregnant, your baby could become dependent on the drug. This can cause life-threatening withdrawal symptoms in the baby after it is born. Babies born dependent on habit-forming medicine may need medical treatment for several weeks. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
This medicine can pass into breast milk and may harm a nursing baby. Tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding a baby.
Not approved for use by anyone younger than 12 years old.
How should I take acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine?
Follow all directions on your prescription label. Do not take more of this medication than recommended. An overdose can damage your liver or cause death. Tell your doctor if the medicine seems to stop working as well in relieving your pain.
Butalbital may be habit-forming. Never share acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine with another person, especially someone with a history of drug abuse or addiction. Keep the medication in a place where others cannot get to it. Selling or giving away this medicine is against the law.
Store at room temperature away from moisture and heat.
Keep track of the amount of medicine used from each new bottle. Butalbital is a drug of abuse and you should be aware if anyone is using your medicine improperly or without a prescription.
What happens if I miss a dose?
Since this medicine is used when needed, you may not be on a dosing schedule. If you are on a schedule, use the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not use extra medicine to make up the missed dose.
What happens if I overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. An overdose of acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine can be fatal.
The first signs of an acetaminophen overdose include loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, sweating, and confusion or weakness. Later symptoms may include pain in your upper stomach, dark urine, and yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes.
Overdose symptoms may also include insomnia, restlessness, tremor, diarrhea, increased shallow breathing, uneven heartbeats, seizure (convulsions), or fainting.
What should I avoid while taking acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine?
This medication can cause side effects that may impair your thinking or reactions. Be careful if you drive or do anything that requires you to be awake and alert.
Avoid drinking alcohol. It may increase your risk of liver damage while taking acetaminophen.
Ask a doctor or pharmacist before using any other cold, allergy, pain, or sleep medication. Acetaminophen (sometimes abbreviated as APAP) is contained in many combination medicines. Taking certain products together can cause you to get too much acetaminophen which can lead to a fatal overdose. Check the label to see if a medicine contains acetaminophen or APAP.
While you are taking this medication, avoid taking diet pills, caffeine pills, or other stimulants (such as ADHD medications) without your doctor’s advice.
Acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine side effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
In rare cases, acetaminophen may cause a severe skin reaction that can be fatal. This could occur even if you have taken acetaminophen in the past and had no reaction. Stop taking acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine and call your doctor right away if you have skin redness or a rash that spreads and causes blistering and peeling. If you have this type of reaction, you should never again take any medicine that contains acetaminophen.
This medicine may cause serious side effects. Stop using this medicine and call your doctor at once if you have:
- confusion, a seizure;
- shortness of breath;
- a light-headed feeling, like you might pass out; or
- nausea, upper stomach pain, itching, loss of appetite, dark urine, clay-colored stools, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
Common side effects of acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine may include:
- drowsiness, dizziness;
- feeling light-headed;
- nausea, vomiting, stomach pain;
- drunk feeling; or
- shortness of breath.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine dosing information
Usual Adult Dose for Headache:
Butalbital 50 mg/acetaminophen 300 mg/caffeine 40 mg: 1 or 2 capsules orally every 4 hours as needed not to exceed 6 capsules per day
Butalbital 50 mg/acetaminophen 325 mg/caffeine 40 mg: 1 or 2 capsules or tablets orally every 4 hours as needed not to exceed 6 capsules or tablets per day
Butalbital 50 mg/acetaminophen 325 mg/caffeine per 15 mL oral liquid: 15 to 30 mL orally every 4 hours as needed not to exceed 90 mL per day
Comments:
-Due to high rate of physical dependence, the extended use of this drug is not recommended.
-The safety and efficacy of treating multiple recurrent headaches with this product is not known.
Uses: For the relief of the symptom complex of tension (or muscle contraction) headache.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Headache:
12 years or older:
Butalbital 50 mg/acetaminophen 300 mg/caffeine 40 mg: 1 or 2 capsules orally every 4 hours as needed not to exceed 6 capsules per day
Butalbital 50 mg/acetaminophen 325 mg/caffeine 40 mg: 1 or 2 capsules or tablets orally every 4 hours as needed not to exceed 6 capsules or tablets per day
Butalbital 50 mg/acetaminophen 325 mg/caffeine per 15 mL oral liquid: 15 to 30 mL orally every 4 hours as needed not to exceed 90 mL per day
Comments:
-Due to high rate of physical dependence, the extended use of this drug is not recommended.
-The safety and efficacy of treating multiple recurrent headaches with this product is not known.
Uses: For the relief of the symptom complex of tension (or muscle contraction) headache.
What other drugs will affect acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine?
Taking this medicine with other drugs that make you sleepy or slow your breathing can cause dangerous or life-threatening side effects. Ask your doctor before taking acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine with a sleeping pill, opioid pain medicine, muscle relaxer, or medicine for anxiety, depression, or seizures.
Other drugs may affect acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Tell your doctor about all other medicines you use.
Where can I get more information?
Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use this medication only for the indication prescribed.
More about acetaminophen / butalbital / caffeine
- Check interactions
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (244)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- Patient tips
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: analgesic combinations
- En español
Patient resources
- Advanced Reading
- Butalbital, Acetaminophen, and Caffeine Capsules and Tablets
- Butalbital, Acetaminophen, and Caffeine Solution
Other brands
Professional resources
Related treatment guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Copyright 1996-2023 Cerner Multum, Inc. Version: 8.01.
Butalbital, Acetaminophen and Caffeine Prescribing Information
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jan 1, 2023.
On This Page
- Boxed Warning
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Indications and Usage
- Contraindications
- Warnings
- Precautions
- Patient Counseling Information
- Drug Interactions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Abuse and Dependence
- Overdosage
- Dosage and Administration
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
Hepatotoxicity
Acetaminophen has been associated with cases of acute liver failure, at times resulting in liver transplant and death. Most of the cases of liver injury are associated with the use of acetaminophen at doses that exceed 4000 milligrams per day, and often involve more than one acetaminophen containing product.
Butalbital, Acetaminophen and Caffeine Description
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, and Caffeine Tablets, USP are supplied in tablet form for oral administration.
Each tablet contains the following active ingredients:
Butalbital, USP 50 mg
Acetaminophen, USP 325 mg
Caffeine, USP 40 mg
Inactive Ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, croscarmellose sodium, corn starch, stearic acid, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, and FD&C Blue No. 1.
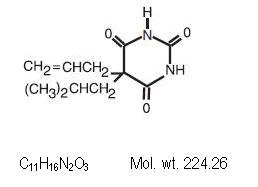
Butalbital (5-allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid), is a short to intermediate-acting barbiturate. It has the following structural formula:
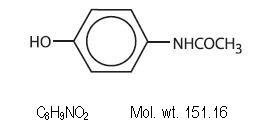
Acetaminophen (4´-hydroxyacetanilide), is a non-opiate, non-salicylate analgesic and antipyretic. It has the following structural formula:
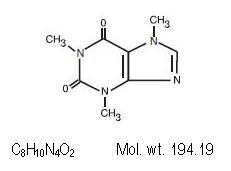
Caffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine), is a central nervous system stimulant. It has the following structural formula:
Related/similar drugs
Butalbital, Acetaminophen and Caffeine – Clinical Pharmacology
This combination drug product is intended as a treatment for tension headache.
It consists of a fixed combination of butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine. The role each component plays in the relief of the complex of symptoms known as tension headache is incompletely understood.
Pharmacokinetics
The behavior of the individual components is described below.
Butalbital is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is expected to distribute to most tissues in the body. Barbiturates in general may appear in breast milk and readily cross the placental barrier. They are bound to plasma and tissue proteins to a varying degree and binding increases directly as a function of lipid solubility.
Elimination of butalbital is primarily via the kidney (59% to 88% of the dose) as unchanged drug or metabolites. The plasma half-life is about 35 hours. Urinary excretion products include parent drug (about 3.6% of the dose), 5-isobutyl-5-(2, 3-dihydroxypropyl) barbituric acid (about 24% of the dose), 5-allyl-5(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-propyl) barbituric acid (about 4.8% of the dose), products with the barbituric acid ring hydrolyzed with excretion of urea (about 14% of the dose), as well as unidentified materials. Of the material excreted in the urine, 32% is conjugated.
The in vitro plasma protein binding of butalbital is 45% over the concentration range of 0.5-20 mcg/mL. This falls within the range of plasma protein binding (20%-45%) reported with other barbiturates such as phenobarbital, pentobarbital, and secobarbital sodium. The plasma-to-blood concentration ratio was almost unity, indicating that there is no preferential distribution of butalbital into either plasma or blood cells.
See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is distributed throughout most body tissues. The plasma half-life is 1.25 to 3 hours, but may be increased by liver damage and following overdosage. Elimination of acetaminophen is principally by liver metabolism (conjugation) and subsequent renal excretion of metabolites. Approximately 85% of an oral dose appears in the urine within 24 hours of administration, most as the glucuronide conjugate, with small amounts of other conjugates and unchanged drug.
See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Like most xanthines, caffeine is rapidly absorbed and distributed in all body tissues and fluids, including the CNS, fetal tissues, and breast milk.
Caffeine is cleared through metabolism and excretion in the urine. The plasma half-life is about 3 hours. Hepatic biotransformation prior to excretion results in about equal amounts of 1-methylxanthine and 1-methyluric acid. Of the 70% of the dose that is recovered in the urine, only 3% is unchanged drug.
See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Indications and Usage for Butalbital, Acetaminophen and Caffeine
Butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine tablets, USP are indicated for the relief of the symptom complex of tension (or muscle contraction) headache.
Evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of this combination product in the treatment of multiple recurrent headaches is unavailable. Caution in this regard is required because butalbital is habit-forming and potentially abusable.
Contraindications
This product is contraindicated under the following conditions:
– Hypersensitivity or intolerance to any component of this product
– Patients with porphyria.
Warnings
Hepatotoxicity
Acetaminophen has been associated with cases of acute liver failure, at times resulting in liver transplant and death. Most of the cases of liver injury are associated with the use of acetaminophen at doses that exceed 4000 milligrams per day, and often involve more than one acetaminophen containing product. The excessive intake of acetaminophen may be intentional to cause self-harm or unintentional as patients attempt to obtain more pain relief or unknowingly take other acetaminophen-containing products.
The risk of acute liver failure is higher in individuals with underlying liver disease and in individuals who ingest alcohol while taking acetaminophen.
Instruct patients to look for acetaminophen or APAP on package labels and not to use more than one product that contains acetaminophen. Instruct patients to seek medical attention immediately upon ingestion of more than 4000 milligrams of acetaminophen per day, even if they feel well.
Serious Skin Reactions
Rarely, acetaminophen may cause serious skin reactions such as acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. Patients should be informed about the signs of serious reactions, and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Hypersensitivity/anaphylaxis
There have been post-marketing reports of hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis associated with use of acetaminophen. Clinical signs included swelling of the face, mouth, and throat, respiratory distress, urticaria, rash, pruritus, and vomiting. There were infrequent reports of life-threatening anaphylaxis requiring emergency medical attention. Instruct patients to discontinue butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine tablets, USP immediately and seek medical care if they experience these symptoms. Do not prescribe butalbital, aceta‑minophen, and caffeine tablets, USP for patients with acetaminophen allergy.
Butalbital is habit-forming and potentially abusable. Consequently, the extended use of this product is not recommended.
Precautions
General
Butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine tablets, USP should be prescribed with caution in certain special-risk patients, such as the elderly or debilitated, and those with severe impairment of renal or hepatic function, or acute abdominal conditions.
Information for Patients/Caregivers
This product may impair mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery. Such tasks should be avoided while taking this product.
Alcohol and other CNS depressants may produce an additive CNS depression when taken with this combination product, and should be avoided.
Butalbital may be habit-forming. Patients should take the drug only for as long as it is prescribed, in the amounts prescribed, and no more frequently than prescribed.
For information on use in geriatric patients, see PRECAUTIONS/Geriatric Use .
• Do not take butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine tablets, USP if you are allergic to any of its ingredients. • If you develop signs of allergy such as a rash or difficulty breathing stop taking butal‑bital, acetaminophen, and caffeine tablets, USP and contact your healthcare provider immediately. • Do not take more than 4000 milligrams of acetaminophen per day. Call your doctor if you took more than the recommended dose.
Laboratory Tests
In patients with severe hepatic or renal disease, effects of therapy should be monitored with serial liver and/or renal function tests.
Drug Interactions
The CNS effects of butalbital may be enhanced by monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors.
Butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine may enhance the effects of: other narcotic analgesics, alcohol, general anesthetics, tranquilizers such as chlordiazepoxide, sedative-hypnotics, or other CNS depressants, causing increased CNS depression.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Acetaminophen may produce false-positive test results for urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No adequate studies have been conducted in animals to determine whether acetaminophen or butalbital have a potential for carcinogenesis, mutagenesis or impairment of fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with this combination product. It is also not known whether butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. This product should be given to a pregnant woman only when clearly needed.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Withdrawal seizures were reported in a two-day-old male infant whose mother had taken a butalbital-containing drug during the last two months of pregnancy. Butalbital was found in the infant’s serum. The infant was given phenobarbital 5 mg/kg, which was tapered without further seizure or other withdrawal symptoms.
Nursing Mothers
Caffeine, barbiturates, and acetaminophen are excreted in breast milk in small amounts, but the significance of their effects on nursing infants is not known. Because of potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 12 have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine tablets, USP did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Butalbital is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Adverse Reactions
Frequently Observed
The most frequently reported adverse reactions are drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and intoxicated feeling.
Infrequently Observed
All adverse events tabulated below are classified as infrequent.
Central Nervous System: headache, shaky feeling, tingling, agitation, fainting, fatigue, heavy eyelids, high energy, hot spells, numbness, sluggishness, seizure. Mental confusion, excitement, or depression can also occur due to intolerance, particularly in elderly or debilitated patients, or due to overdosage of butalbital.
Autonomic Nervous System: dry mouth, hyperhidrosis.
Gastrointestinal: difficulty swallowing, heartburn, flatulence, constipation.
Musculoskeletal: leg pain, muscle fatigue.
Miscellaneous: pruritus, fever, earache, nasal congestion, tinnitus, euphoria, allergic reactions.
Several cases of dermatological reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme, have been reported.
The following adverse drug events may be borne in mind as potential effects of the components of this product. Potential effects of high dosage are listed in the OVERDOSAGE section.
Acetaminophen: allergic reactions, rash, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis.
Caffeine: cardiac stimulation, irritability, tremor, dependence, nephrotoxicity, hyperglycemia.
Drug Abuse and Dependence
Abuse and Dependence
Butalbital
Barbiturates may be habit-forming: Tolerance, psychological dependence, and physical dependence may occur especially following prolonged use of high doses of barbiturates. The average daily dose for the barbiturate addict is usually about 1500 mg. As tolerance to barbiturates develops, the amount needed to maintain the same level of intoxication increases; tolerance to a fatal dosage, however, does not increase more than two-fold. As this occurs, the margin between an intoxication dosage and fatal dosage becomes smaller. The lethal dose of a barbiturate is far less if alcohol is also ingested. Major withdrawal symptoms (convulsions and delirium) may occur within 16 hours and last up to 5 days after abrupt cessation of these drugs. Intensity of withdrawal symptoms gradually declines over a period of approximately 15 days. Treatment of barbiturate dependence consists of cautious and gradual withdrawal of the drug. Barbiturate-dependent patients can be withdrawn by using a number of different withdrawal regimens. One method involves initiating treatment at the patient’s regular dosage level and gradually decreasing the daily dosage as tolerated by the patient.
Overdosage
Following an acute overdosage of butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine, toxicity may result from the barbiturate or the acetaminophen. Toxicity due to caffeine is less likely, due to the relatively small amounts in this formulation.
Signs and Symptoms
Toxicity from barbiturate poisoning include drowsiness, confusion, and coma; respiratory depression; hypotension; and hypovolemic shock.
In acetaminophen overdosage: dose-dependent, potentially fatal hepatic necrosis is the most serious adverse effect. Renal tubular necrosis, hypoglycemic coma, and coagulation defects may also occur. Early symptoms following a potentially hepatotoxic overdose may include: nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, and general malaise. Clinical and laboratory evidence of hepatic toxicity may not be apparent until 48 to 72 hours post-ingestion. In adults hepatic toxicity has rarely been reported with acute overdoses of less than 10 grams, or fatalities with less than 15 grams.
Acute caffeine poisoning may cause insomnia, restlessness, tremor, and delirium, tachycardia and extrasystoles.
Treatment
A single or multiple overdose with this combination product is a potentially lethal polydrug overdose, and consultation with a regional poison control center is recommended.
Immediate treatment includes support of cardiorespiratory function and measures to reduce drug absorption. Oxygen, intravenous fluids, vasopressors, and other supportive measures should be employed as indicated. Assisted or controlled ventilation should also be considered.
Gastric decontamination with activated charcoal should be administered just prior to N-acetylcysteine (NAC) to decrease systemic absorption if acetaminophen ingestion is known or suspected to have occurred within a few hours of presentation. Serum acetaminophen levels should be obtained immediately if the patient presents 4 hours or more after ingestion to assess potential risk of hepatotoxicity; acetaminophen levels drawn less than 4 hours post-ingestion may be misleading. To obtain the best possible outcome, NAC should be administered as soon as possible where impending or evolving liver injury is suspected. Intravenous NAC may be administered when circumstances preclude oral administration.
Vigorous supportive therapy is required in severe intoxication. Procedures to limit the continuing absorption of the drug must be readily performed since the hepatic injury is dose dependent and occurs early in the course of intoxication.
Butalbital, Acetaminophen and Caffeine Dosage and Administration
One or 2 tablets every 4 hours as needed. Total daily dosage should not exceed 6 tablets.
Extended and repeated use of this product is not recommended because of the potential for physical dependence.
How is Butalbital, Acetaminophen and Caffeine Supplied
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, and Caffeine Tablets, USP contain 50 mg butalbital, 325 mg acetaminophen, and 40 mg caffeine.
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, and Caffeine Tablets USP, 50 mg/325mg/40 mg are light-blue, speckled, round uncoated tablets, debossed “1695” on one side and “LCI” on the other side and are supplied in:
Overbagged with 10 tablets per bag, NDC 55154-3356-0
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required).
Distributed by:
Lannett Company, Inc.
Philadelphia, PA 19136
Dublin, OH 43017
Made in the USA
Package/Label Display Panel
Butalbital, Acetaminophen and Caffeine Tablets, USP
50 mg/ 325 mg/ 40 mg

| Product Information | |||
| Product Type | HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL | Item Code (Source) | NDC:55154-3356(NDC:0904-6938) |
| Route of Administration | ORAL | DEA Schedule | |
| Active Ingredient/Active Moiety | ||
| Ingredient Name | Basis of Strength | Strength |
| BUTALBITAL (BUTALBITAL) | BUTALBITAL | 50 mg |
| ACETAMINOPHEN (ACETAMINOPHEN) | ACETAMINOPHEN | 325 mg |
| CAFFEINE (CAFFEINE) | CAFFEINE | 40 mg |
| Inactive Ingredients | |
| Ingredient Name | Strength |
| MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE | |
| CROSPOVIDONE | |
| CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM | |
| STARCH, CORN | |
| STEARIC ACID | |
| SILICON DIOXIDE | |
| MAGNESIUM STEARATE | |
| FD&C BLUE NO. 1 | |
| Product Characteristics | |||
| Color | BLUE (Light-blue, speckled) | Score | no score |
| Shape | ROUND | Size | 11mm |
| Flavor | Imprint Code | LCI;1695 | |
| Contains | |||
| Packaging | |||
| # | Item Code | Package Description | |
| 1 | NDC:55154-3356-0 | 10 BLISTER PACK in 1 BAG | |
| 1 | 1 TABLET in 1 BLISTER PACK | ||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| ANDA | ANDA200243 | 09/13/2012 | |
| Labeler – Cardinal Health 107, LLC (118546603) |
Cardinal Health 107, LLC
More about acetaminophen / butalbital / caffeine
- Check interactions
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (244)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- Patient tips
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: analgesic combinations
- En español
Patient resources
Professional resources
- Prescribing Information
- Butalbital,Acetaminophen and Caffeine Solution (FDA)
