Clindamycin Gel
If you have these symptoms, do not use anti-diarrhea or opioid products because they may make symptoms worse.
Clindamycin Phosphate Gel – Uses, Side Effects, and More
This medication is used to treat acne. It helps to decrease the number of acne lesions. Clindamycin is an antibiotic which works by stopping the growth of bacteria.
How to use Clindamycin Phosphate Gel
Use this medication only on the skin. Clean and dry the affected area first. Follow all directions on the product package, or use as directed by your doctor.
If you are using the lotion, shake the bottle well before using. Apply a thin layer of medication usually twice a day or as directed by your doctor.
If you are using the medicated pad or swab, apply to the the affected area gently with it, then discard. Depending on the size of the area to be treated, more than one pad or swab may be necessary.
If you are using the foam, apply it once daily to the affected areas. Use enough to cover the entire affected area. Do not spray the foam directly onto your hands or face, because the foam will begin to melt on contact with warm skin. Instead spray the amount needed directly into the cap or onto a cool surface such as a counter top. If the can seems warm or the foam seems runny, run the can under cold water. Please read the patient information leaflet available from your pharmacist for specific instructions on how to use the foam, and ask about any information that is unclear.
As of August 2020, the most expensive drug in America is Myalept, a drug used to treat leptin deficiency. A month’s worse of this drug costs $71, 306 per month, according to research from GoodRx. Myalept is known as an “orphan drug” because it’s intended to treat a rare disease.
Avoid contact with your eyes, nose, mouth or any areas of broken skin. If you accidentally get medication in these areas, rinse well with plenty of cool water.
It may take between 2-6 weeks to notice an improvement in your condition, and up to 12 weeks to see the full benefit.
Inform your doctor if your condition does not improve or worsens.
Side Effects
Burning, itching, dryness, redness, oily skin or skin peeling may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.
This medication may be absorbed into your bloodstream and very rarely cause a severe intestinal condition due to a bacteria called C. difficile. This condition may occur during treatment or weeks to months after treatment has stopped. Tell your doctor right away if you develop: diarrhea that doesn’t stop, abdominal or stomach pain/cramping, blood/mucus in your stool.
If you have these symptoms, do not use anti-diarrhea or opioid products because they may make symptoms worse.
A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
In the US – Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.
In Canada – Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
Precautions
Before using clindamycin, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or to lincomycin; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.
Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: chronic asthma or hay fever (atopic conditions), intestinal diseases (such as ulcerative colitis, enteritis, C. difficile-associated diarrhea).
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant before using this medication.
It is not known if the medication in this product passes into breast milk. While there have been no reports of harm to nursing infants, consult your doctor before breast-feeding.
Interactions
Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor’s approval.
Clindamycin Gel
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 1, 2022.
On This Page
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Clinical Studies
- Indications and Usage
- Contraindications
- Warnings
- Precautions
- Drug Interactions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Overdosage
- Dosage and Administration
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
Clindamycin Gel Description
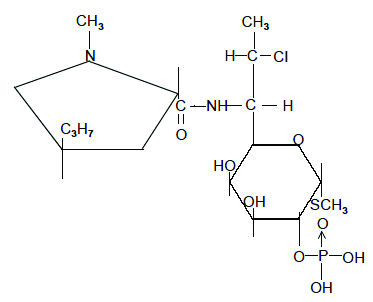
Clindamycin phosphate gel USP, 1%, a topical antibiotic, contains clindamycin phosphate, USP, at a concentration equivalent to 10 mg clindamycin per gram in a gel vehicle consisting of propylene glycol, polyethylene glycol 400, methylparaben, carbomer homopolymer type A, sodium hydroxide and purified water. Chemically, clindamycin phosphate, USP is a water-soluble ester of the semi-synthetic antibiotic produced by a 7 (S)-chloro-substitution of the 7 (R)-hydroxyl group of the parent antibiotic, lincomycin, and has the structural formula represented below:
The chemical name for clindamycin phosphate, USP is methyl 7-chloro-6,7,8-trideoxy-6-(1-methyl- trans -4-propyl-L-2-pyrrolidinecarboxamido)-1-thio-L- threo -α-D- galacto -octopyranoside 2-(dihydrogen phosphate).
Clindamycin Gel – Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
In an open label, parallel group study of 24 patients with acne vulgaris, once-daily topical administration of approximately 3 to 12 grams/day of clindamycin phosphate gel for five days resulted in peak plasma clindamycin concentrations that were less than 5.5 ng/ml.
Following multiple applications of clindamycin phosphate gel less than 0.04% of the total dose was excreted in the urine.
Although clindamycin phosphate is inactive in vitro , rapid in vitro hydrolysis converts this compound to clindamycin which has antibacterial activity. Clindamycin inhibits bacteria protein synthesis at the ribosomal level by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and affecting the process of peptide chain initiation. In vitro studies indicated that clindamycin inhibited all tested Propionibacterium acnes cultures at a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 0.4 mcg/ml. Cross-resistance has been demonstrated between clindamycin and erythromycin.
Clinical Studies
In one 12-week, multicenter, randomized, evaluator-blind, vehicle-controlled, parallel comparison clinical trial in which patients used clindamycin phosphate gel, 1% once daily or the vehicle gel once daily, in the treatment of acne vulgaris of mild to moderate severity, clindamycin phosphate gel applied once daily was more effective than the vehicle applied once daily. The mean percent reductions in lesion counts at the end of treatment in this study are shown in the following table:
Clindamycin Phosphate Gel
QD
N=162
Vehicle Gel
QD
N=82
There was a trend in the investigator’s global assessment of the results which favored clindamycin phosphate gel QD over the vehicle QD.
In a contact sensitization study, four of the 200 subjects appeared to develop suggestive evidence of allergic contact sensitization to clindamycin phosphate gel. There was no signal for contact sensitization in the clinical trials under normal use conditions.
Indications and Usage for Clindamycin Gel
Clindamycin phosphate gel, 1% is indicated for topical application in the treatment of acne vulgaris. In view of the potential for diarrhea, bloody diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis, the physician should consider whether other agents are more appropriate (see CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and ADVERSE REACTIONS ).
Contraindications
Clindamycin phosphate gel is contraindicated in individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to preparations containing clindamycin or lincomycin, a history of regional enteritis or ulcerative colitis, or a history of antibiotic-associated colitis.
Warnings
Orally and parenterally administered clindamycin has been associated with severe colitis, which may result in patient death. Use of the topical formulation of clindamycin results in absorption of the antibiotic from the skin surface. Diarrhea, bloody diarrhea, and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported with the use of topical and systemic clindamycin.
Studies indicate a toxin(s) produced by Clostridia is one primary cause of antibiotic-associated colitis. The colitis is usually characterized by severe persistent diarrhea and severe abdominal cramps and may be associated with the passage of blood and mucus. Endoscopic examination may reveal pseudomembranous colitis. Stool culture for Clostridium difficile and stool assay for C. difficile toxin may be helpful diagnostically.
When significant diarrhea occurs, the drug should be discontinued. Large bowel endoscopy should be considered to establish a definitive diagnosis in cases of severe diarrhea. Antiperistaltic agents, such as opiates and diphenoxylate with atropine, may prolong and/or worsen the condition.
Diarrhea, colitis, and pseudomembranous colitis have been observed to begin up to several weeks following cessation of oral and parenteral therapy with clindamycin.
Precautions
General
Clindamycin phosphate gel should be prescribed with caution in atopic individuals.
Drug Interactions
Clindamycin has been shown to have neuromuscular blocking properties that may enhance the action of other neuromuscular blocking agents. Therefore, it should be used with caution in patients receiving such agents.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenicity of a 1% clindamycin phosphate gel similar to clindamycin phosphate gel was evaluated by daily application to mice for two years. The daily doses used in this study were approximately 3 and 15 times higher than the human dose of clindamycin phosphate from 5 milliliters of clindamycin phosphate gel, assuming complete absorption and based on a body surface area comparison. No significant increase in tumors was noted in the treated animals.
A 1% clindamycin phosphate gel similar to clindamycin phosphate gel caused a statistically significant shortening of the median time to tumor onset in a study in hairless mice in which tumors were induced by exposure to simulated sunlight.
Genotoxicity tests performed included a rat micronucleus test and an Ames Salmonella reversion test. Both tests were negative.
Reproduction studies in rats using oral doses of clindamycin hydrochloride and clindamycin palmitate hydrochloride have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility.
Pregnancy: Teratogenic effects
Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and mice using subcutaneous and oral doses of clindamycin phosphate, clindamycin hydrochloride and clindamycin palmitate hydrochloride. These studies revealed no evidence of fetal harm. The highest dose used in the rat and mouse teratogenicity studies was equivalent to a clindamycin phosphate dose of 432 mg/kg. For a rat, this dose is 84 fold higher, and for a mouse 42 fold higher, than the anticipated human dose of clindamycin phosphate from clindamycin phosphate gel based on a mg/m 2 comparison. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether clindamycin is excreted in human milk following use of clindamycin phosphate gel. However, orally and parenterally administered clindamycin has been reported to appear in breast milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in children under the age of 12 have not been established.
Geriatric Use
The clinical study with clindamycin phosphate gel did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine if they respond differently than younger patients.
Adverse Reactions
In the one well-controlled clinical study comparing clindamycin phosphate gel and its vehicle, the incidence of skin and appendages adverse events occurring in ≥1% of the patients in either group is presented below:
Number (%) of Patients
Body System/Adverse Event
Clindamycin Phosphate Gel
QD
(N=168)
Vehicle Gel
QD
(N=84)
Skin and appendages disorders
Clindamycin Phosphate(Topical) Gel – Uses, Side Effects, and More
This medication is used to treat acne. It helps to decrease the number of acne lesions. Clindamycin is an antibiotic which works by stopping the growth of bacteria.
How to use Clindamycin Phosphate(Topical) Gel
Use this medication only on the skin. Clean and dry the affected area first. Follow all directions on the product package, or use as directed by your doctor.
If you are using the lotion, shake the bottle well before using. Apply a thin layer of medication usually twice a day or as directed by your doctor.
If you are using the medicated pad or swab, apply to the the affected area gently with it, then discard. Depending on the size of the area to be treated, more than one pad or swab may be necessary.
If you are using the foam, apply it once daily to the affected areas. Use enough to cover the entire affected area. Do not spray the foam directly onto your hands or face, because the foam will begin to melt on contact with warm skin. Instead spray the amount needed directly into the cap or onto a cool surface such as a counter top. If the can seems warm or the foam seems runny, run the can under cold water. Please read the patient information leaflet available from your pharmacist for specific instructions on how to use the foam, and ask about any information that is unclear.
Avoid contact with your eyes, nose, mouth or any areas of broken skin. If you accidentally get medication in these areas, rinse well with plenty of cool water.
It may take between 2-6 weeks to notice an improvement in your condition, and up to 12 weeks to see the full benefit.
Inform your doctor if your condition does not improve or worsens.
Side Effects
Burning, itching, dryness, redness, oily skin or skin peeling may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.
This medication may be absorbed into your bloodstream and very rarely cause a severe intestinal condition due to a bacteria called C. difficile. This condition may occur during treatment or weeks to months after treatment has stopped. Tell your doctor right away if you develop: diarrhea that doesn’t stop, abdominal or stomach pain/cramping, blood/mucus in your stool.
If you have these symptoms, do not use anti-diarrhea or opioid products because they may make symptoms worse.
A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
In the US – Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.
In Canada – Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
Precautions
Before using clindamycin, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or to lincomycin; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.
Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: chronic asthma or hay fever (atopic conditions), intestinal diseases (such as ulcerative colitis, enteritis, C. difficile-associated diarrhea).
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant before using this medication.
It is not known if the medication in this product passes into breast milk. While there have been no reports of harm to nursing infants, consult your doctor before breast-feeding.
Interactions
Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor’s approval.